What Is the Difference Between the Green and Blue Wrat4 Forms
Introduction
The Wide Range Achievement Test 4 is the test that is aimed at testing students' basic academic skills, the competency in reading, spelling, sentence comprehension, and mathematics. The test is directed at people from 5 up to 94 years old. The WRA has two forms Blue and Green, pretest, and posttest. The possibilities to report the results, organize those in a form of a table or chart are useful (Hebben & Milberg, 2009).
The WRAT 4 is the test which helps quickly check students' academic knowledge. This test is simple, but its usefulness should not be underestimated. It helps to diagnose learning disabilities if any and check students' progress in studying. Moreover, teachers may use this test to determine which skills they should pay more attention to. Getting down to the researched-based critique on the Wide Range Achievement Test 4, the following information should be considered, norms, reliability, validity, properties of the test instrument, history, and practical utility in detail.
The Wide Range Achievement Test 4
Developmental norms
The developmental norms of WRAT 4 are based on age and grade scores, as well as "percentile ranks, as well as optional stanines, normal curve equivalents (NCEs), grade equivalents, and Rasch ability scaled scores" (Makray, C., & Hope, 2009, p. 50). The standardization procedure is considered to be the most important part of the development of the test. To follow this procedure, about 3,000 people were used as samples for collecting necessary information.
The subjects of the standardization were from different age groups (from 5 to 94), of various gender, race/ethnicity, and level of knowledge. The main purpose of the appendices in the test devoted to Blue, Green, and Combined forms is to make the test more universal, without the dependence on geography or students' age. Due to those the test is able to measure the individual performance of each student separately (Makray, C., & Hope, 2009).
Reliability
The test is reliable as it covers not only the data considered from the competencies tests, but it also calculates the standard error of measurement, including internal consistency. Moreover, the test covers immediate and delayed retest stability as well as the standard score confidence intervals. All this information helps the test to be reliable.
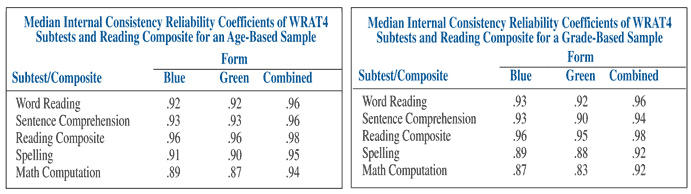
Turning to the close consideration of each measure, it is possible to state the following ranges.
- "Median internal consistency coefficients across ages for each of the alternate forms used individually range from.87 to.96" (Wilkinson & Robertson, 2010b, n/p)
- "Median internal consistency coefficients across ages for each of the alternate forms combined range from.94 to.96" (Wilkinson & Robertson, 2010b, n/p).
- "Alternate form immediate re-test reliabilities range from.78-.89 for an age-based sample and from.86-.90 for a grade-based sample" (Wilkinson & Robertson, 2010b, n/p).
- "Alternate form delayed re-test study indicates that practice effects are quite small. The mean score difference was 0.4-2.2 for an age-based sample and 0.1-0.5 for a grade-based sample (Wilkinson & Robertson, 2010b, n/p).
Validity
The main purpose of the validity in any test is "cumulative and ongoing process" (p. 52). It is important to mention that the first variant of the WRAT test was developed in 1946 and has come through several stages to become WRAT 4. Being based on the previous versions of the test, it is important to mention that sentence comprehension is a new subtest which was not used in the previous versions.
The validity of the test is based on the following evidence, "content and development of the subtests", "increase in mean subtest scores in successive age levels", "intercorrelations amongst subtests", "item Bias or Differential Item Functioning", "correlation of the WRAT4 with other measures of cognitive ability and achievement" (Makray, C., & Hope, 2009, p. 52). Due to the fact that the test is highly valid, there are some specific reasons when it cannot be used. Due to the description for the test, it does not require a Level A certificate which obligatory for similar products if they are used in the UK. Thus, the test does not correspond to the requirements of the UK administration and cannot be used there.
Properties of the test instrument
One of the main properties of the test is the ability to monitor students' progress in four different fields of knowledge. Moreover, WRAT 4 can be used not only for educational purposes but also to measure clinical results. Psychologists can easily offer their patients to pass the test and measure whether they have any learning disabilities or not. Students are given 30 up to 45 minutes to answer the questions in the test which are aimed at covering the information for the evaluation of four basic skills.
History
The first WRAT was published in 1946 by Joseph Jastak. Before the creation of the WRAT 4, there were a number of versions that were considered to be better. Thus, WRAT-R and WRAT 3 have been used before. One of the main purposes of each version, including WRAT 4, was the evaluation of students' cognitive abilities. The first versions combined only reading spelling, and calculation as the basic skills for measurement (Makray & Hope, 2009).
Practical utility
According to Roid & Ledbetter (2010), the test is designed "particularly for underachievers in regular education placements, those diagnosed with learning difficulties, those enrolled in special education, or those with conditions that affect the ability to learn" (par. 1). Moreover, as it was mentioned above WRAT 4 is the best tool for teachers to predict the information in which teachers should practice more. Teachers can also follow students' success and notice some problems in time.
Conclusion
General valuation of the test
In conclusion, it should be mentioned that the test is a real help for teachers and psychologists. Being improved and upgraded in relation to the previous versions, it measures not only reading, spelling, and calculation abilities of people aged from 5 up to 94 years old but also sentence comprehension. Three forms, Bleu (pretest), Green (posttest), and combined forms make it possible to evaluate the progress that is really important in the modern educational system.
Personal reflection
The WRAT 4 should be used as the basis for the evaluation of students in every educational establishment. Having come through serious standardization, it is considered to be valid and reliable not only in education but also for measuring clinical results. The possibility to summarize the information in charts and diagrams makes it possible to compare and contrast the results obtained in different years.
Reference List
Hebben, N. & Milberg, W. (2009). Essentials of Neuropsychological Assessment. New York: John Wiley and Sons.
Makray, C., & Hope, G. (2009).Test Review: Wide Range Achievement Test (WRAT4). Journal of Occupational Psychology, Employment and Disability, Vol 11, No 1, pp. 49-55.
Roid, G. H. & Ledbetter, M. F. (2010). WRAT4–PMV™: Wide Range Achievement Test 4–Progress Monitoring Version. Multi-Health Systems Inc. Web.
Wilkinson, G. S., & Robertson, G. J. (2010a). Wide Range Achievement Test 4 (WRAT4). PAR. Web.
Wilkinson, G. S., & Robertson, G. J. (2010b). WRAT 4 – Wide Range Achievement Test 4. Hogrefe. Web.
Source: https://ivypanda.com/essays/wide-range-achievement-test-4-research-based-critique/
Post a Comment for "What Is the Difference Between the Green and Blue Wrat4 Forms"